Diagrams of the various types of mountain and how they form
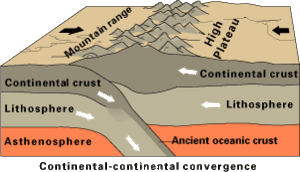
Collision of two continents, which creates mountains such as those stretching from the Himalaya to the Alps.
The Himalaya taken from the Space Shuttle, annotated with the main faults along which the Indian plate slides under Tibet
Courtesy of NASA and Mike Searle
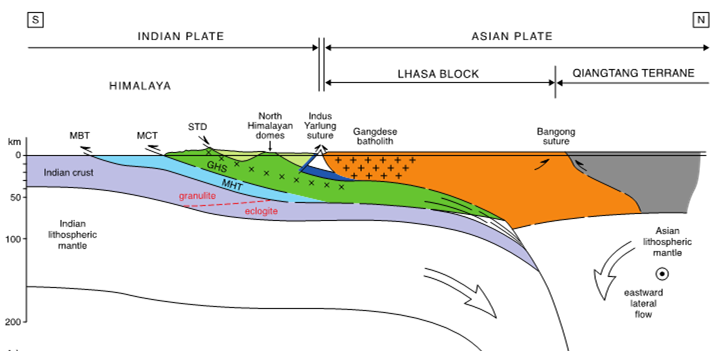
Geological section of the subduction of the Indian plate below the Asian plate. The high Himalaya is shown as in green (GHS: Greater Himalaya Sequence).
Courtesy of Mike Searle
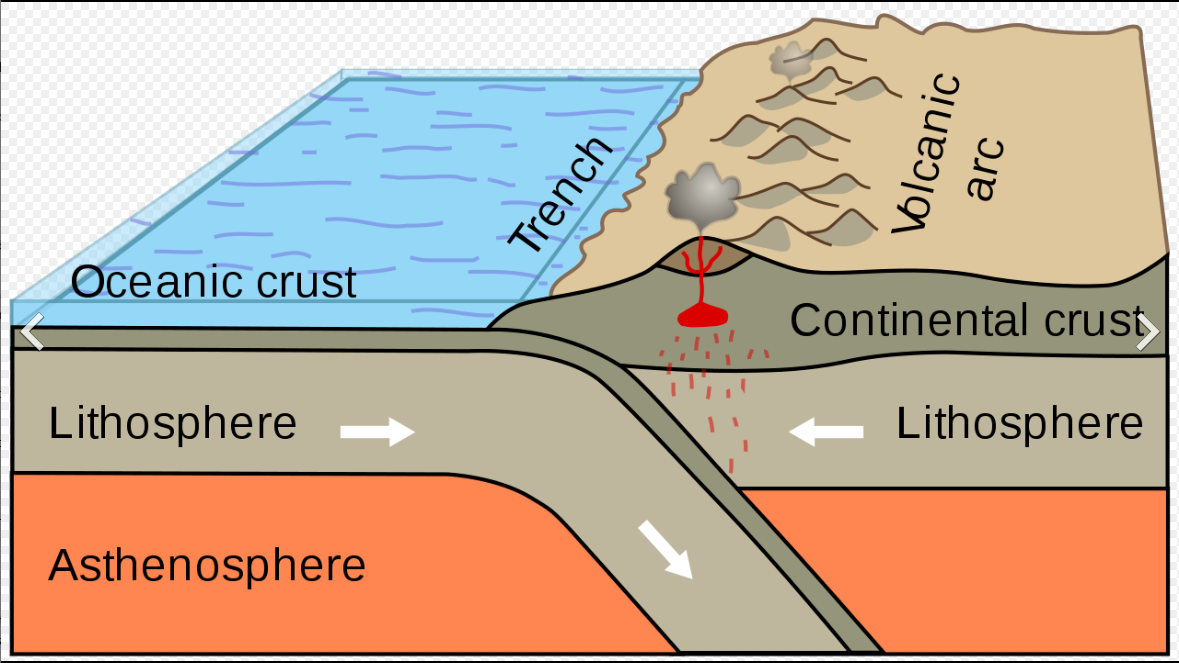
Subduction of an oceanic plate below a continental plate. This produces a chain of volcanoes above the subducted plate, such as the Andes which are being formed by the subduction of the Nazca plate below the South American plate.
A mid-ocean ridge in which new ocean plate crust spreads out on either side of the ridge. An example is the Mid-Atlantic ridge, which is creating new ocean crust and widening the Atlantic.
Rifting of a continental plate to create mountains on either side of the rift. The East African rift valley in Kenya is an example.
In the middle of a plate, volcanoes form over a “hot spot,” which is thought to be a hot plume of mantle that may extend to great depths, approaching the core-mantle boundary at 2900 km. Hot-spot volcanoes in the middle of a plate. The Hawaiian islands are above a hot spot in the Pacific ocean.